What is EGCG?
As we know, tea is one of the most popular drinks in the world. Tea comes from the leaves of the theaceae plant, and according to the different fermentations, it can be divided into non-fermented green tea, semi-fermented oolong tea, fully fermented black tea and so on. Green tea retains the natural structure of its polyphenol compounds and overall components such as catechins, while fully fermented tea contains more oxidized polyphenols such as theaflavins and thearubin. Catechins, such as epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), Epigallocatechin (EGC), Epigallocatechin gallate(ECG) and Epicatechin (EC), these compounds make up more than two-thirds of all tea polyphenols.
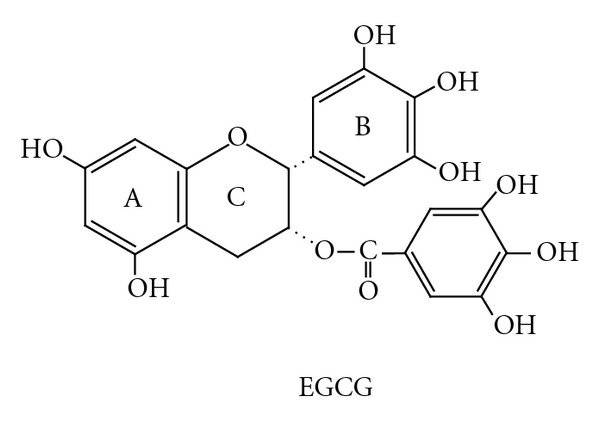
EGCG is a type of catechin, which is a class of flavonoids. EGCG is the most abundant catechin in brewing green tea especially in its fresh and unfermented state, and it’s considered one of the most biologically active and beneficial components of green tea extract. Its chemical structure includes multiple hydroxyl groups and a gallate ester. These features contribute to its antioxidant and potential health-promoting effects. The properties of EGCG include:
Properties of EGCG
Source: Green tea(Camellia sinensis)
Other names: EGCG; (2R, 3R) -5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3, 4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-yl 3 , 4, 5-trihydroxybenzoate
Purity:98%(HPLC)
CAS:84650-60-2
Molecular formula : C22H18O11
Molecular weight: 458.3717
Density:1.9g/cm3
Boiling point:909.1°C at 760 mmHg
Flashpoint :320°C
Vapor pressure :3.71E-35mmHg at 25°C
EGCG is the main component of green tea polyphenols and the main component of green tea catechins, which accounts for 10-15% of the total catechins in green tea, including catechin (EC), epigallocatechin (EGC), Epigallocatechin gallate (ECG) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). Tea polyphenols have strong antioxidant effects, mainly because of the catechin monomer EGCG, whose reducibility can even reach 100 times that of L-isocorbic acid. Among these tea polyphenol catechin monomers, the antioxidant capacity was EGCG, EGC, ECG, EC from the largest to the smallest, and the antioxidant performance increased with the increase of temperature.
The beneficial physiological effects of green tea have been extensively studied, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-cancer, and anti-neurodegenerative properties. EGCG has gained significant attention due to its potential health benefits. What the benefits of EGCG?
Reduce oxidative stress/inflammation
EGCG is a potent antioxidant, which means it can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. This antioxidant activity is believed to contribute to EGCG’s potential health benefits. Studies of EGCG have found that it inhibits the accumulation of reactive oxygen species, alters signaling pathways to prevent excessive inflammatory responses, lowers nitric oxide levels and reduces oxidative stress. There is also evidence that this polyphenol interacts directly with proteins and phospholipids, regulating signal transduction pathways, transcription factors, DNA methylation, mitochondrial function, and autophagy (how the body clears damaged/dead cells). All of this translates into enhanced protection against a variety of health problems, especially those related to inflammation and aging.
Support heart health
The catechins in tea are thought to be beneficial for cardiovascular health. It may help lower levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, reducing the risk of heart disease. According to Harvard Health Press, flavonoids help suppress inflammation, which in turn can reduce plaque buildup in the arteries, improve vascular reactivity, improve blood pressure, and help lower LDL cholesterol levels. There is also evidence that regular tea drinkers have a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.
Helps brain health
Researchers believe that EGCG has a neuroprotective effect, which has antioxidant properties and the ability to protect brain cells from damage and support cognitive function. It has a protective effect against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Studies have found that catechins can help reverse nerve damage and prevent further nerve death, thereby reducing the decline in cognitive function with age. Studies have shown that adults who drink 2-3 cups of green tea daily for several years have a lower risk of cognitive impairment and a 30 to 40 percent lower risk of Parkinson’s disease. In addition to inhibiting cognitive dysfunction, EGCG may also help improve learning by reducing oxidative damage in the brain.
Weight Management
EGCG has been investigated for its potential effect in supporting weight management. It might help increase metabolism and enhance fat oxidation, making it of interest in the context of weight loss. While not a quick way to lose weight, there is some evidence that EGCG can prevent metabolic syndrome and promote fat loss in a number of ways. Such as reducing inflammation, suppressing appetite and increasing energy expenditure. EGCG also works by promoting thermogenesis (the body produces heat through the use of energy). In some studies, drinking two or more cups a day has been linked to better health. For a stronger effect, EGCG and caffeine can be consumed together (from tea or some extract supplements), which can also help to help with fat loss.